Jaguar Sighting Routes in Colombia and Latin America
The jaguar, yaguar o yaguareté (Panthera onca) is recognized as the largest feline in America and the third-largest feline after the tiger and the lion. Besides, Colombia is the third country in Latin America with the largest population of jaguars, after Brazil and Peru. So there is a good chance to see them here!
In this publication, you will get the necessary information about jaguars, and where to discover this wonderful species in Colombia.
Facts About Jaguars
- Their skin is yellow with rosettes and black spots. However, this species sometimes presents melanic variations: black or dark brown individuals, which are called the black panthers.
- The jaguar measures between 1.5 and 2.4 meters, weighs between 45 and 120 kg. and lives between 10 and 12 years. Its body is robust and muscular, with a broad head and small, rounded ears.
- Adult jaguars are solitary, only joining temporarily for a couple of weeks for courtship and copulation. The rutting season lasts 12 days in a 47-day cycle. Ovulation in the female is induced by previous copulation, which stimulates and activates the female’s reproductive system.
- It is theorized that female jaguars may give birth at any time of the year, but the few reports of cubs generally occur between December and March. Sexual maturity is attained at 24-30 months of age.
- Gestation lasts approximately 100 days, and the female gives birth to two or three cubs weighing 800 grams. The cubs are weaned at 4-5 months to begin their carnivorous diet and become independent from their mother between 16 and 24 months of age.
- The jaguar has the most powerful bite of all felines, the intensity of the bite in the attack depends on the prey.
- Unlike other felines, they do not reject water. In fact, they are very good swimmers.
- They are capable of dragging their prey for dozens of meters, even passing it over fallen logs or over wire fences, demonstrating extraordinary strength with their jaws.
- The jaguar also plays a fundamental role in the ecosystem balance, it is capable of guaranteeing the survival of smaller species, and it is an excellent protector of water and forests.
Where do the Jaguar live?
Jaguars can be found in diverse habitats such as forests, wetlands, savannas, and grasslands, from sea level to 3,000m altitude. Current jaguar populations are distributed from Mexico to northern Argentina over an area of 8.75 million km2.
In South America, the number of jaguars exceeds 163 thousand, and Brazil and Peru are the countries with the largest populations of this feline.
Despite this broad range, jaguars have been eradicated from 40 percent of their historic range and are extinct in Uruguay and El Salvador. While the rare individual has been spotted in the US, there has not been evidence of a breeding population in the US in more than 50 years.
The Jaguar is an Endangered Species
There are three causes that endanger the jaguar in the different areas through which it moves:
- The loss of its habitat is due to the use of wildlands for agriculture and other developments. This causes jaguars to run the risk of being isolated in small areas, increasing their risk of extinction.
- Direct hunting by people living in the countryside, who see the jaguar as a threat to their lives and livelihoods.
- The scarcity of natural prey, which is also hunted by humans, has led jaguars to reach areas where they encounter domestic animals for food.
According to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, of the 34 jaguar subpopulations that exist throughout the continent, 33 are Endangered or Critically Endangered. The Amazonian population is the only one in a state of Least Concern.
Recent studies by Panthera Foundation show that there are about 173,000 jaguars remaining in the Americas, less than half of the species that historically existed throughout its range.
The Jaguar Corridor
The jaguar is listed as “Near Threatened” on the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, though its status is in review and may be elevated to “Vulnerable” in the next year.
The species is threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation, conflict with local people due to the real or perceived threat posed to livestock, and overhunting of the jaguar’s prey by local people.
The jaguar corridor is a project showing how big predators can indeed live with humans. Dr. Alan Rabinowitz devoted his life to conserving this magnificent cat and co-founded the Panthera organization, “the only organization in the world that is devoted exclusively to the conservation of the world’s 40 wild cat species and their ecosystems”.
Rabinowitz established the world’s first jaguar sanctuary – the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary – in Belize in 1986. He also developed the conceptualization and implementation of the Jaguar Corridor across their entire range from Mexico to Argentina.
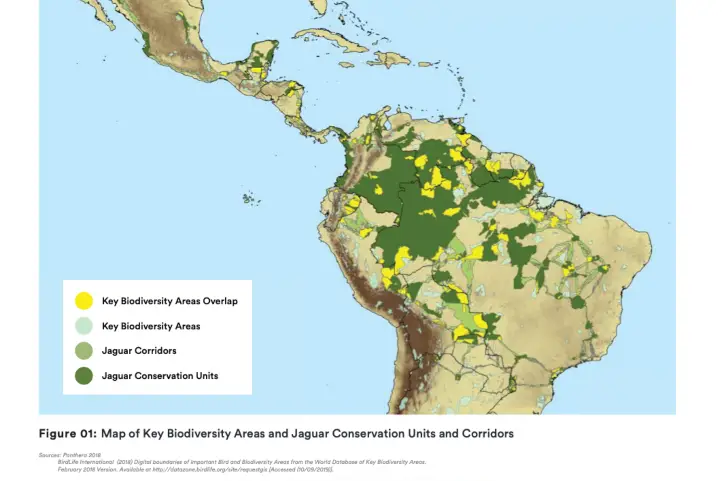
The countries that make up the Jaguar Corridor are: Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, and Bolivia. Besides, the initiative is supported by numerous governments, landowners, corporations, local communities, and scientists.
Currently, the governments of Brazil and Argentina have identified an increase in the jaguar population, which has caused an increase in surveillance and monitoring of border areas in both countries and joint parks to prevent illegal hunters, especially in Iguazu.
Today there is a conservation strategy called Jaguar 2030 Conservation Roadmap for the Americas, a multi-government plan to conserve jaguars across their range supported by UNDP, Panthera, WCS, and WWF. Find out more in the document Jaguar Strategy 2020-2030.
Best Spots to See Jaguars in South America
Jaguars are difficult to spot, as good hunters of prey, they are stealthy animals and camouflage themselves very well. Luck must be on your side!
The most famous destinations for jaguar sightings are:
Brazilian Pantanal.
Jaguars are common to find in the Pantanal ecosystem. 80% of Pantanal is in Brazil, and the remaining 20% is located between Bolivia and Paraguay.
The best spots to see jaguars in Pantanal are in Brazil. In the north, the Cuiabá River is the most known place to watch this animal. Jaguars get exposed during the dry season, from June to October, when they visit the riverbanks to hunt capybara and caiman.
Towards the southern Pantanal, there is the Caiman Lodge, the Onçafari Project fosters ecotourism, monitors wild jaguars, and releases rescued cats into the wild.
The Amazon Jungle in Peru
Manú National Park is a biosphere reserve, a hot spot of biodiversity, where you can see jaguars. Besides, this reserve is a great destination for birdwatching.
The tropical forest of the Guiana Shield in Guyana
The place is famous since the BBC filmed its series Lost Land Of The Jaguar in 2008.
The tropical cloud forest of Belize
In Belize, you will find the first nature reserve created to protect jaguars, it is called Cockscomb, a sanctuary located in central Belize.
Eastern Plains in Colombia
In Casanare, in Hato La Aurora, in Hato Corozal, in the Ariporo and Orinoco River Basin, are the places where jaguars can be free and protected thanks to the support of the community.
In this area there is natural prey such as armadillos, deer, and others that are not found in any habitat, that is to say, that where the Jaguar is, it acts as a protector of these species and those that are not seen such as insects, invertebrates and plants that are within an ecosystem.
Colombia is a favorite place for jaguar conservation
Jaguar populations inhabit forests below 2,000 m.a.s.l., in tropical forests, riparian and gallery forests associated with rivers, marshes and beaches, tropical savannahs; they are also found in montane forests.
In Colombia, there are four blocks of large populations, in decreasing size: Amazon, Orinoco, biogeographic Choco, and the Caribbean. Jaguars’ distribution in the national territory follows like this:
- 4.2 jaguars per 100 km2 in Amacayacu National Natural Park.
- 2.8 jaguars per 100 km2 in unprotected Amazonian rainforests.
- Populations of 3.2 adults/100 km2 for an oil palm landscape in the Magdalena Medio region.
- 1.9 adults/100 km2 for the Colombian Llanos.
The biological corridor in Colombia covers 228.000 hectares and protects the lives of 34 species of medium and large mammals; it is the most important and largest in the countries where the jaguar is present.
Besides, there are videographic records in different areas of the country where you can see the presence of the jaguar in its natural habitat, which has led to studies for conservation.
Today, Colombia launched its first Jaguar Sighting Route, a conservation – tourism project which aim is to strengthen Colombia as a jaguar sighting destination. The project includes the creation of a guide to good practices for cat watching, training of local guides, and the creation of trails and a portfolio of services associated with nature tourism. Find out more in our entry The Top Post-Covid-19 Destinations for Conservation Lovers in Colombia.
References
- http://reporte.humboldt.org.co/biodiversidad/2015/cap3/306/#seccion7
- http://www.wildllanos.com/la-aurora-tour.html
- https://fundacion-jaguar.org/en/informacion-del-jaguar.php
- https://www.panthera.org/cms/sites/default/files/Panthera_Fact-Sheet_Jaguar.pdf
About the author
Luisa Martin
Engineer, world traveler, amateur photographer, traveling blogger, and foody.